Before becoming the product it is today, Rocket Remote Desktop underwent multiple changes of ownership. It started as VisionApp Remote Desktop (vRD), made available around 2005. vRD was sold to Allen Systems Group (ASG) in 2011, was purchased by Rocket Software in 2021, and finally became Rocket Remote Desktop. Rocket Remote Desktop helps IT teams, independent professionals, and administrators manage remote connections with a file-based sharing system, a variety of protocols (including the industry standard, RDP), and the option to store connections in a SQL database.
Devolutions Remote Desktop Manager (RDM) has extensive remote connection protocol support and organization features. RDM boasts advanced data sources ideal for individuals and teams, and includes many of the same features as Rocket Remote Desktop. Let’s explore how the features and functionalities of these two products compare, given their similarities.
The Many Remote Connection Protocols
Rocket Remote Desktop has limited protocol support compared to others in the industry. It only allows RDP, ICA, VNC, SSH, or Telnet connections. This limitation may force organizations whose environments require a variety of connection protocols to supplement Rocket Remote Desktop with other software.
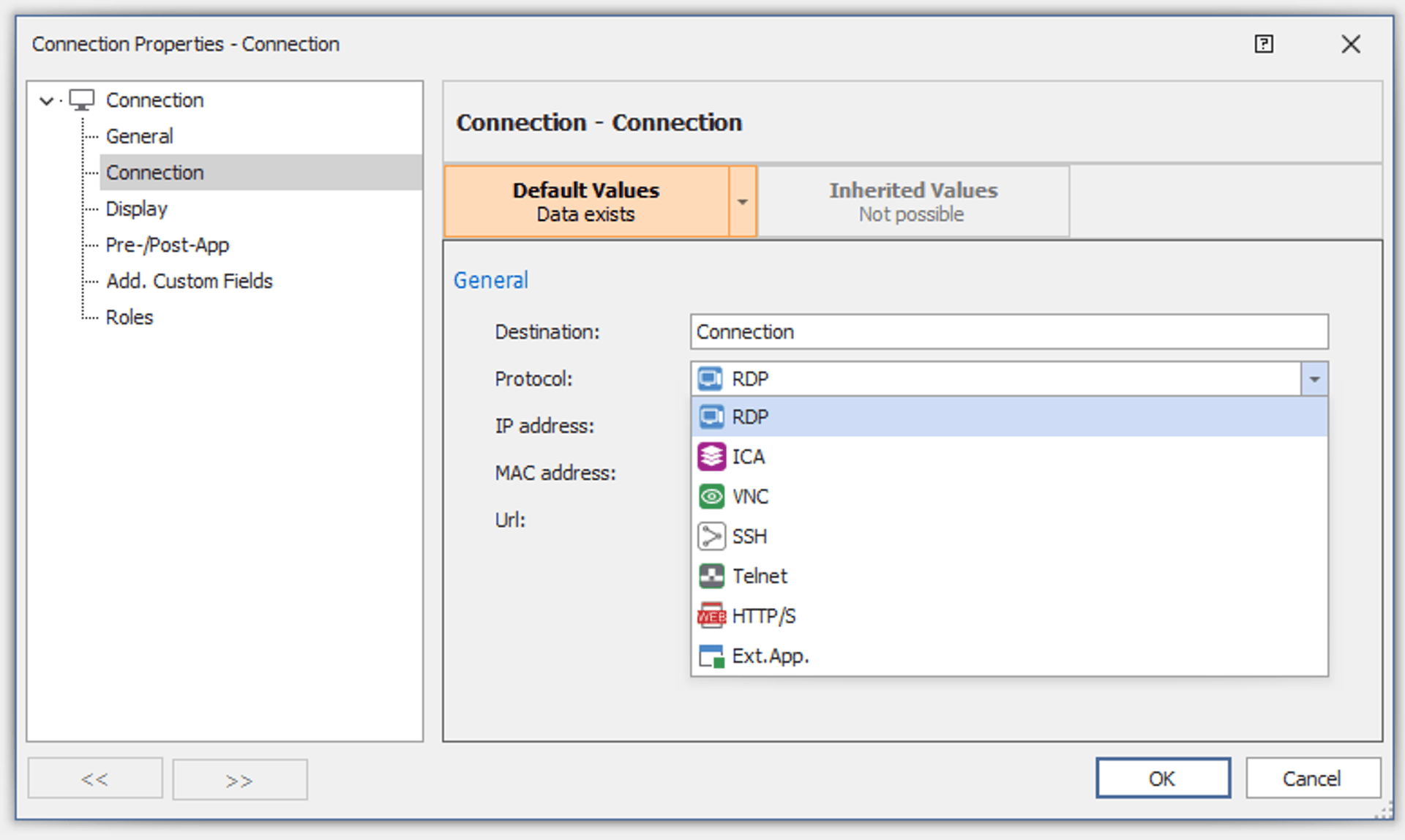
In comparison, RDM supports more remote connection protocols than most other tools like it. In addition to the connection protocols offered by Rocket Remote Desktop, RDM includes TeamViewer, AnyDesk, Citrix, DameWare, LogmeIn, Radmin, and X Window connection types.
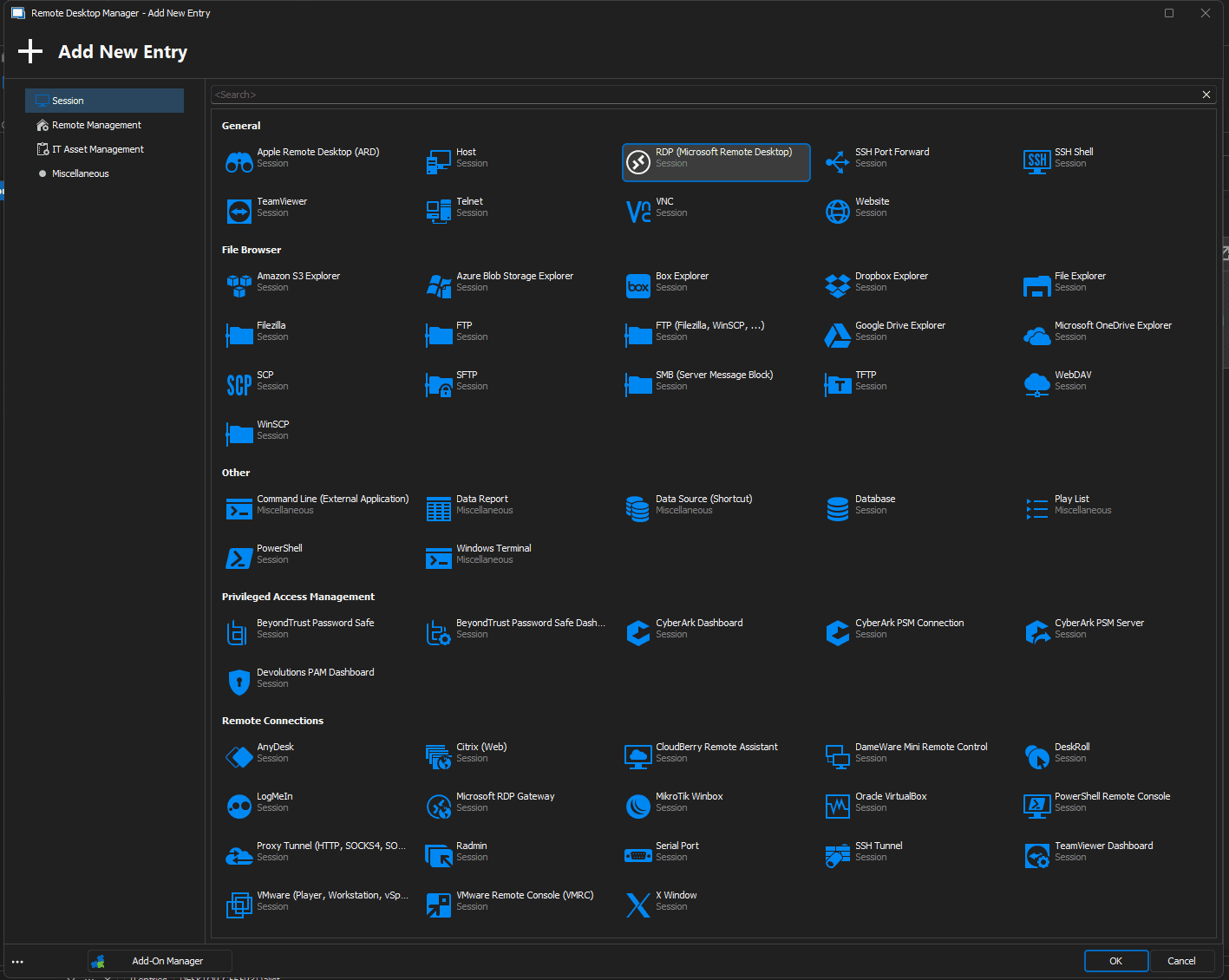
Unlike Rocket Remote Desktop, RDM also offers dashboard interfaces for VMware, Hyper-V, Active Directory, Amazon AWS, and Splunk. With these multiple connections and dashboard interfaces, RDM becomes the one-stop shop for most IT administrative need.
Supporting Microsoft RDP
Like many other remote desktop software, Rocket Remote Desktop offers RDP support through a built-in Windows ActiveX control. The downside of this method is that it restricts RDP capability to the version of operating system on which the application runs.
An odd design choice requires users to select both the connection type and a role of the same kind before being able to access the specific properties of the connection. Although this two-step process is cumbersome, it does unlock additional RDP connection properties.
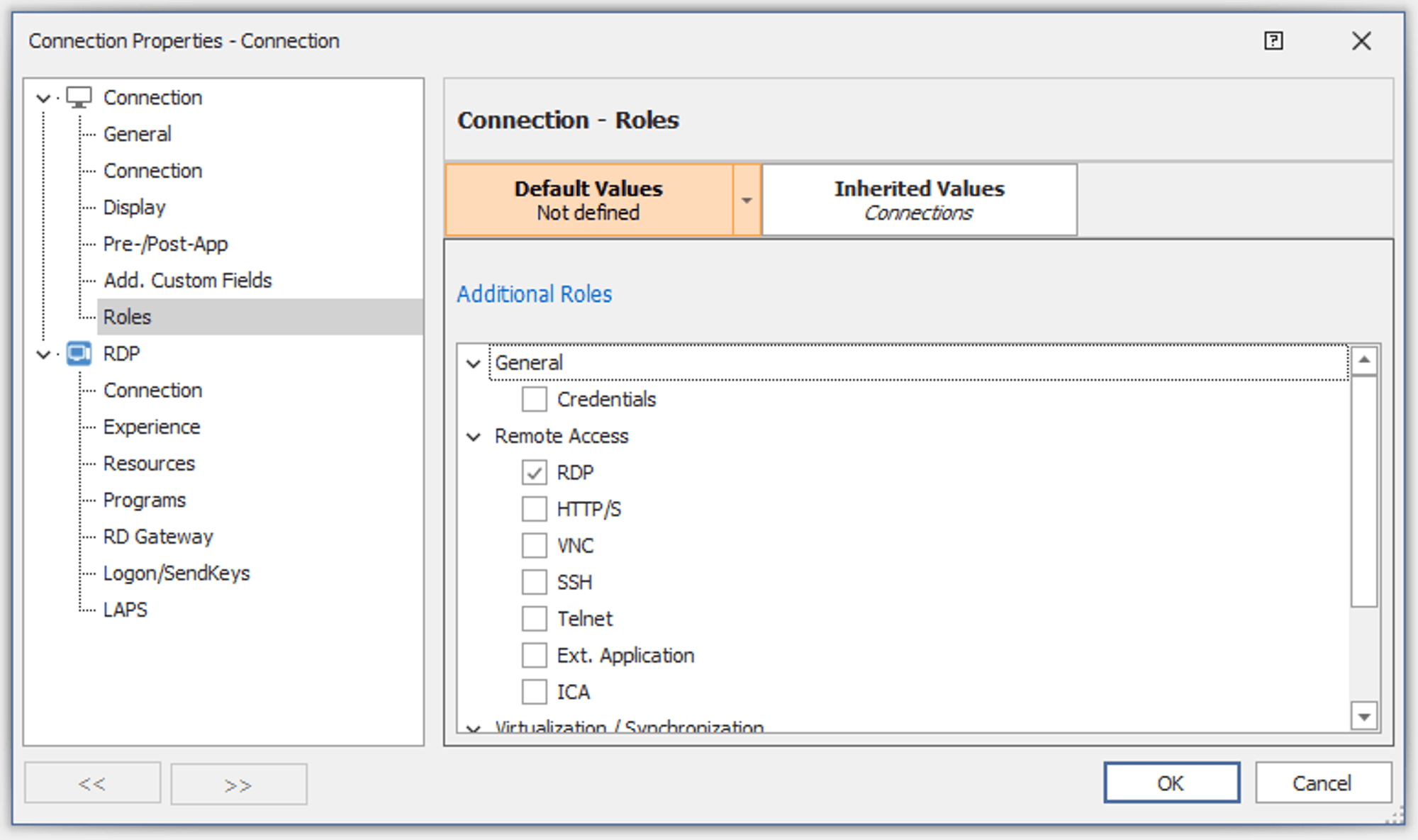
Rocket Remote Desktop offers settings typical for an RDP connection, with one difference: settings for LAPS (Local Administrator Password Solution). In environments where LAPS is used, the remote system could be connected to using the local administrator account thanks to the LAPS feature, which automatically reads the generated password from Active Directory, simplifying the connection process.
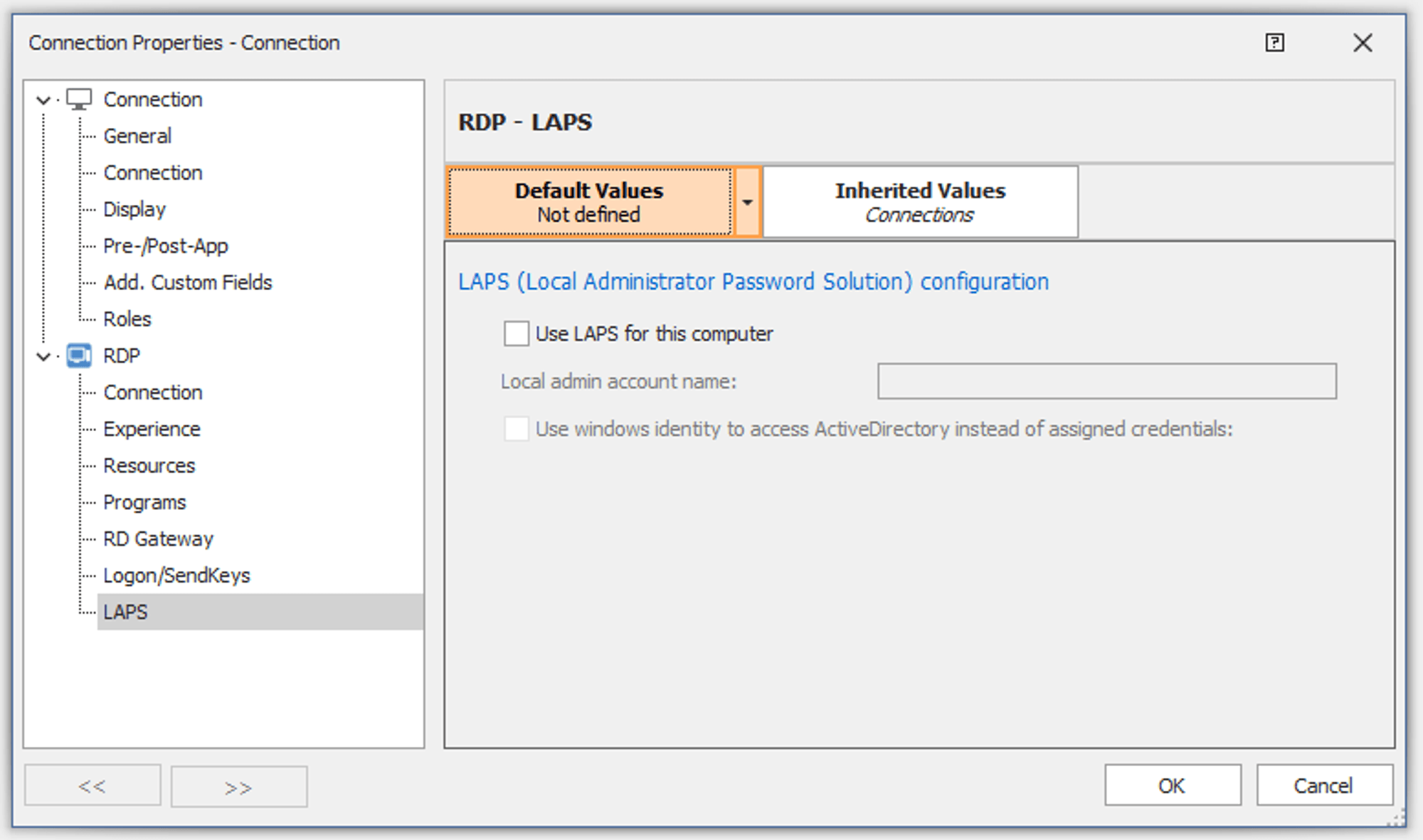
Different from Rocket Remote Desktop, Devolutions RDM supports several implementations of RDP. Any of the following RDP implementations can be chosen when connecting to a remote RDP source:
- A specific version of RDP, running the ActiveX control of that RDP version
- MSRDC, a modernized version of MSTSC, primarily intended for Azure Virtual Desktop connections
- A cross-platform RDP implementation in FreeRDP, which also supports the latest version of RDP, 10.11
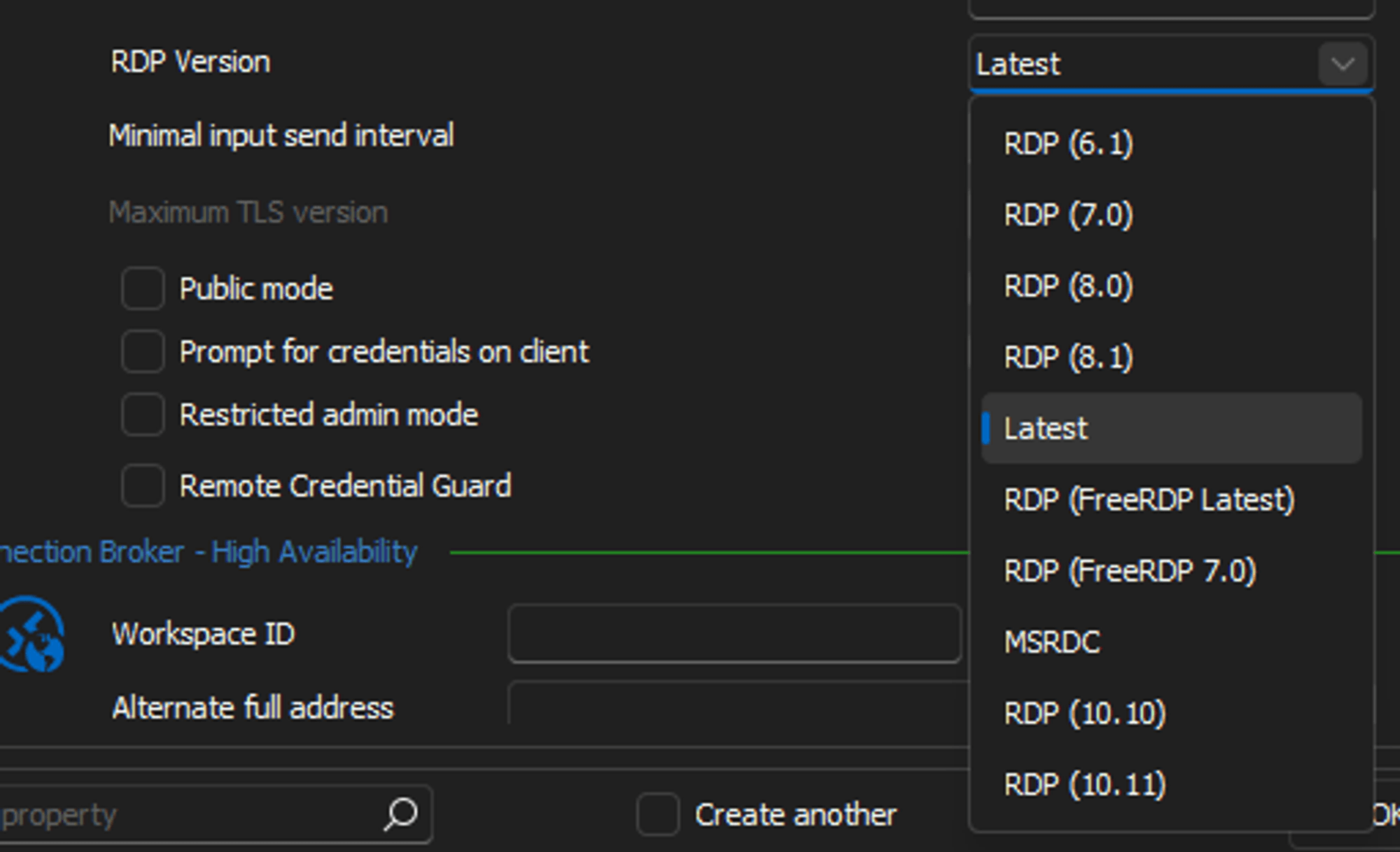
RDM offers flexibility in running modern RDP versions on even the oldest systems, thanks to RDM’s multiple built-in RDP implementations. In practical terms, any bugs that crop up can be bypassed by simply switching to a different version or implementation.
Although Microsoft typically controls RDP, RDM has implemented API hooking to fix issues and add features that would otherwise be unavailable. More details about can be found in this blog post.
Keeping it Clean: Organizing Connections
Rocket Remote Desktop uses environments to organize connections. Each environment can be contained within a file or a SQL database. Different connections can be compartmentalized within environments based on the user or team's needs.
In folders, not only are the icons customizable, but entries can be inherited. Nearly all settings can be inherited from folders, rather than needing to be duplicated. This robust inheritance capability is one of the strongest merits of Rocket Remote Desktop.
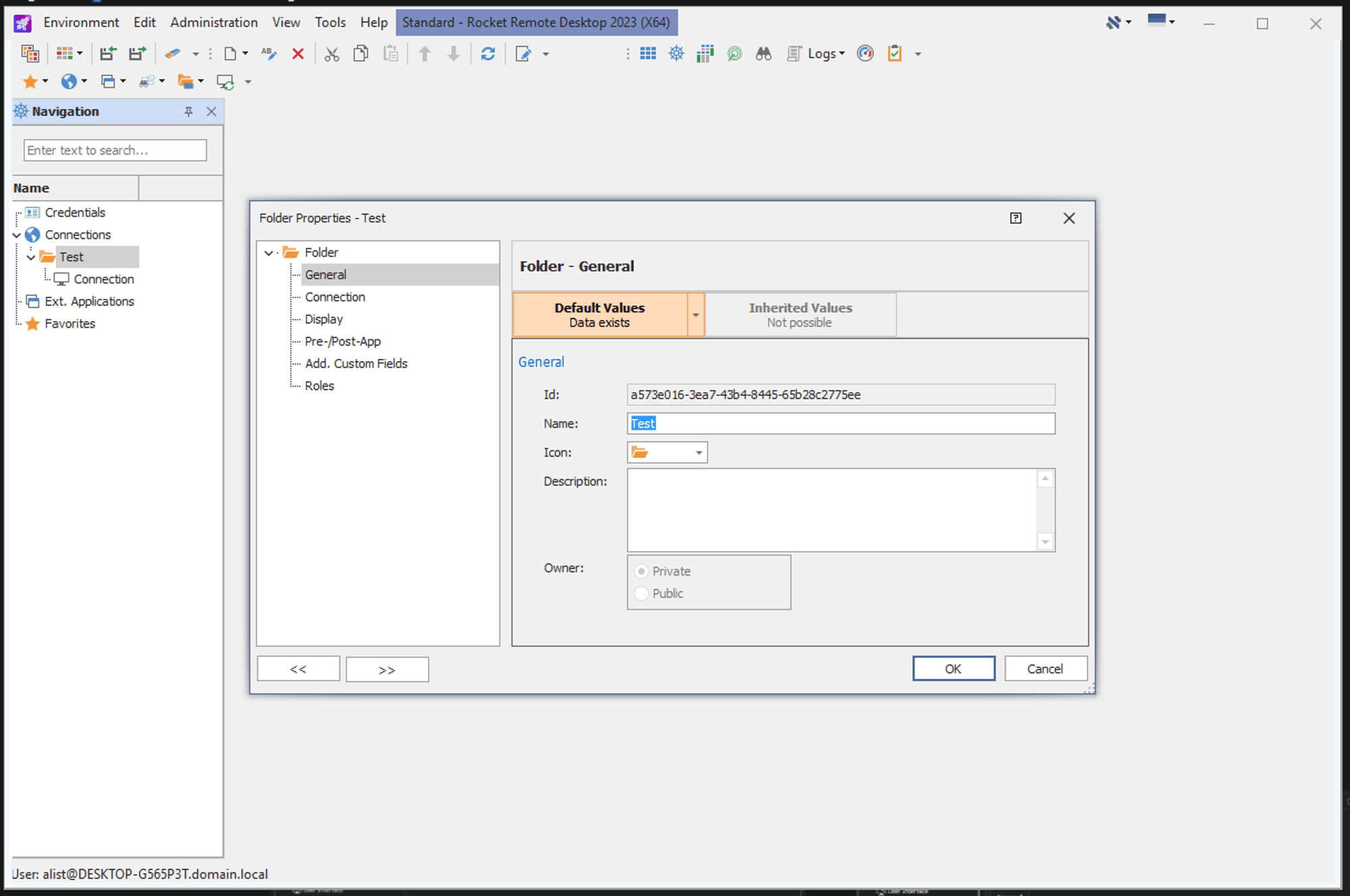
In addition to standard organizational abilities, Rocket Remote Desktop supports credential linking. You must create a credential first and then link that credential to an entry if you want to save the authentication for a connection. This required disassociation between connections and credentials has pros and cons, notably the ease of updating credentials.
Whereas Rocket Remote Desktop structures content based on individual or shared environments (shared through a SQL database) with limited permissions, Devolutions RDM offers more options for organizing remote connections, credentials, and other entries.
Devolutions RDM uses vaults, ranging from simple to advanced, that offer control and security over their contents. For advanced data source vaults, RDM provides enhanced reporting and permission control. To make finding content in RMD easy, content can be tagged, icons and colors can be customized, and descriptions can be added to connections and folders.
Using tags and naming schemes, Smart Group folders can automatically group connections based on defined criteria.
For truly customizable connections, RDM offers the following features (beyond what Rocket Remote Desktop offers):
- Tab Groups as an alternative to a thumbnail view
- Playlists to open saved sets of connections as needed
- Folder Icons and Colors along with individual Entry (connection) Icons and Colors.
Support from Anywhere
Rocket Remote Desktop is currently only Windows-compatible and not cross-platform. This means that professionals operating on Linux or macOS, or mobile clients such as iOS and Android, will not be able to manage their remote sessions using this software.
With Devolutions RDM, IT emergencies can be dealt with from nearly any device. RDM provides a client for Windows, macOS, and Linux. Additionally, it has a mobile client for Android and iOS, so that teams can navigate any scenario.
Staying Secure in an Insecure World
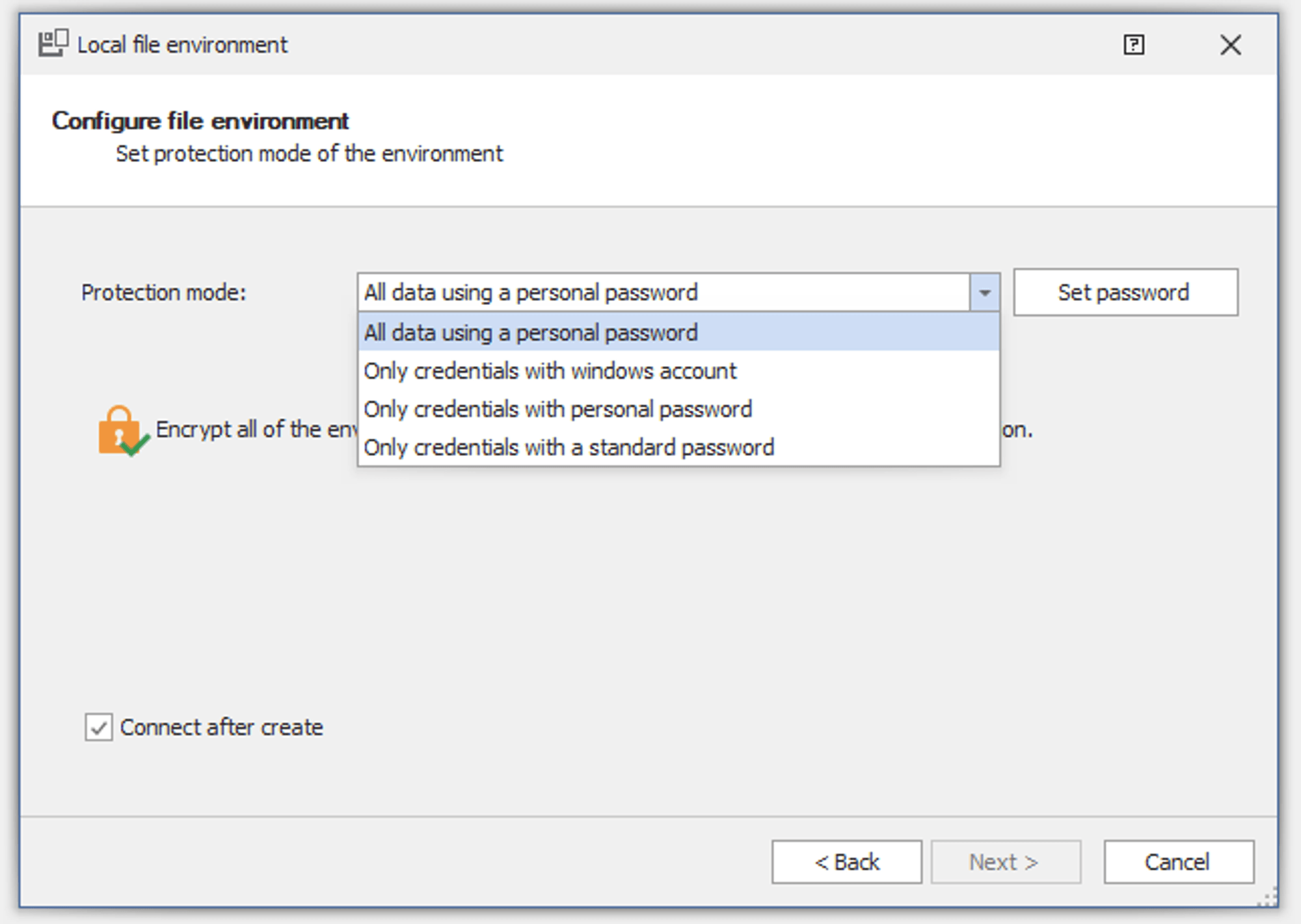
For every environment, Rocket Remote Desktop offers the following data encryption modes:
- All data using a personal password
- Only credentials with a Windows account
- Only credentials with a personal password
- Only credentials with a standard password
The first option fully encrypts the entire XML file. However, the other schemes encrypt only the credentials. Database entries are encrypted when the user logs into the environment through Windows Authentication or through an internal user and password combination.
Devolutions RDM uses AES 256-bit encryption to secure all sensitive information, such as credentials. RDM can also fully encrypt all data using flexible security providers. With the addition of Advanced Data Sources, such as MSSQL, Azure SQL, and Devolutions Server, organizations can implement comprehensive auditing, logging, and RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) for their teams. Devolutions RDM offers in-depth security standard support, enabling organizations to stay compliant and secure.
Which One? Rocket Remote Desktop vs. Devolutions RDM
Although similar to Devolutions RDM when it comes to remote connection organization, Rocket Remote Desktop's protocol limitations and team management capabilities make it better suited to individuals rather than teams.
| Feature | Rocket Remote Desktop | Devolutions Remote Desktop Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Remote Desktop Protocol | X | X |
| Folder Organization | X | X |
| Stored Credentials | X | X |
| Additional Protocols (SSH, VNC, etc.) | X | X |
| Role-Based Access Control | X | |
| Enhanced Metadata (Tagging, Images, Colors, etc.) | X | X |
| Cross-Platform Client | X | |
| Multiple RDP Version Support | X | |
| Team Support through Advanced Data Sources | X | X |
In comparison, Devolutions RDM provides comprehensive support for a variety of remote connection protocols. For teams with a distributed workforce (which is becoming increasingly common), RDM offers a client for almost every platform. RDM integrates with Advanced Data Sources for compliance with security standards and helps teams with advanced user permission control.